WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF COMPUTER NETWORK?
Computer networks are classified into different categories based on their size, coverage, and intended use. The four primary types of computer networks include:
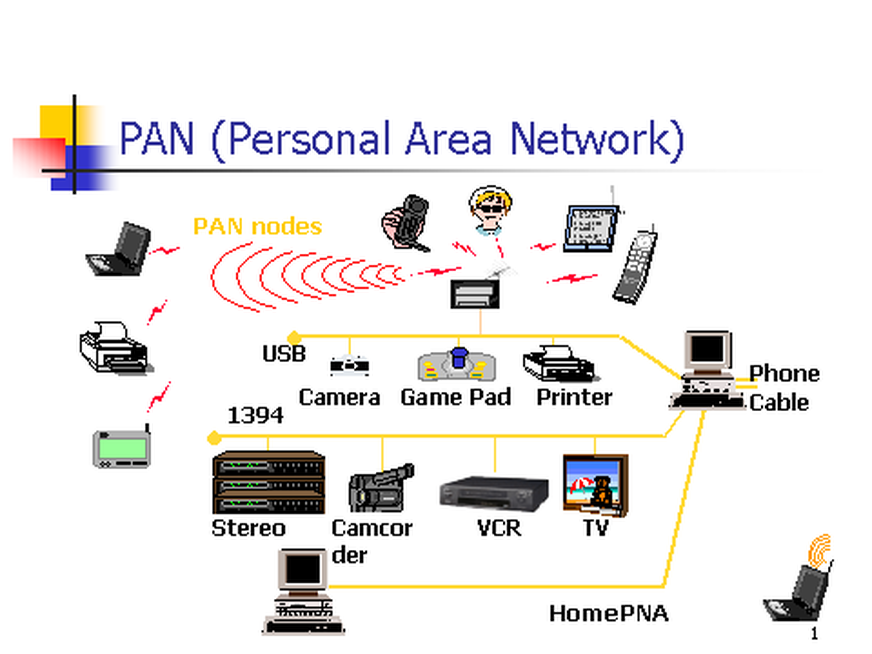
1. Personal Area Network (PAN):
A PAN is the smallest type of network, typically covering a short range, usually within a few meters.
It's designed for connecting devices like smartphones, tablets, laptops, and peripherals (e.g., Bluetooth-enabled headphones or keyboards) in a personal space.
Common technologies for PANs include Bluetooth and Wi-Fi Direct.
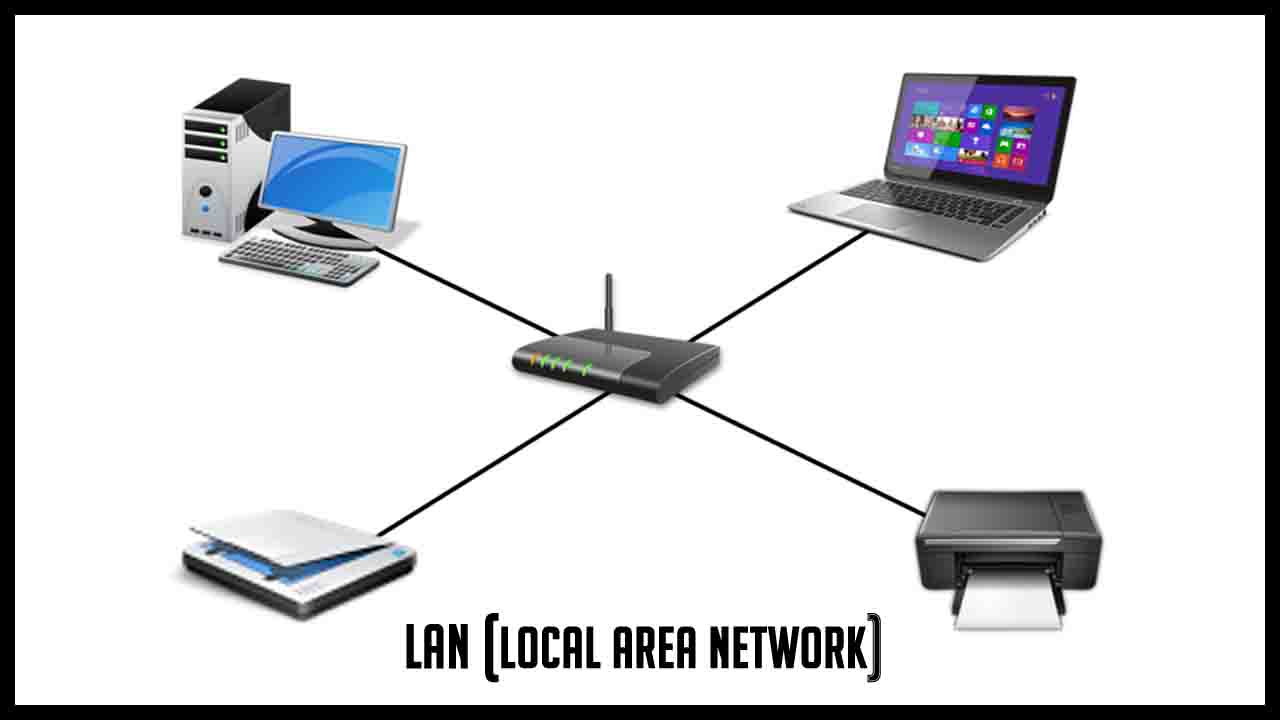
2. Local Area Network (LAN):
LANs encompass a relatively small geographical area, such as a single building, office, or campus.
They connect devices within this limited area, facilitating resource sharing like file sharing, printing, and internet access.
Common technologies used in LANs include Ethernet and Wi-Fi.
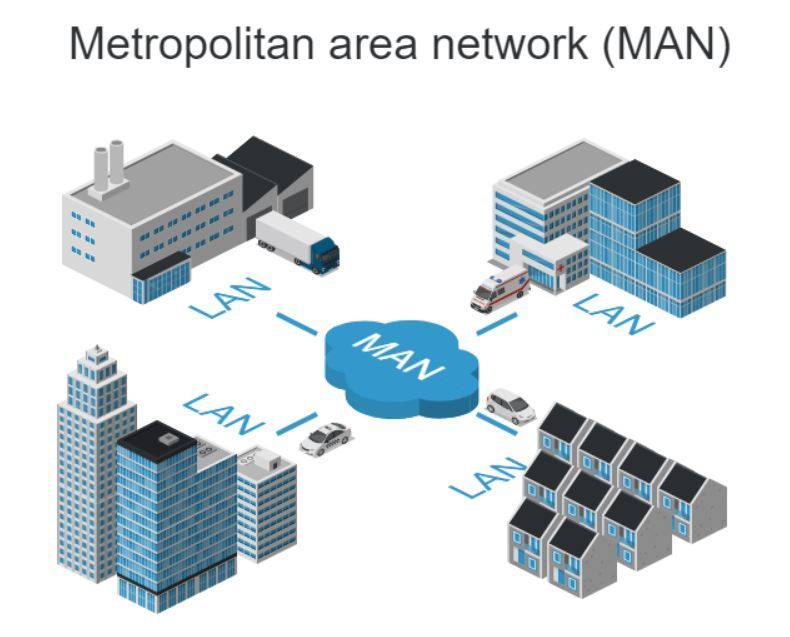
3. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN):
A MAN covers a larger geographical area than a LAN but is still confined to a specific city or metropolitan region.
It links multiple LANs within the same city, offering higher data transfer speeds and wider coverage compared to LANs.
MANs are often employed by businesses and organizations with multiple branches in a city.
4. Wide Area Network (WAN):
WANs span a vast geographical area, often extending across cities, countries, or continents.
They are used for long-distance communication and connect various LANs and MANs over an extensive area.
The internet itself is the largest example of a WAN, and technologies such as leased lines, satellite links, and VPNs establish WAN connections.

These network types differ in terms of size, range, and the technologies used to establish and maintain them, each serving distinct communication needs. Additionally, there are specialized network types like Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), Intranets, and Extranets that fulfill specific purposes within the broader context of computer networking.
.jpg)

Comments
Post a Comment